What is reflux and how to prevent it?
WHAT IS REFLUX?
Reflux is the process where stomach contents flow back into the esophagus. During this process, stomach acid or food from the stomach moves upward into the upper digestive tract, causing unpleasant sensations such as a burning feeling (heartburn), a sour taste in the mouth, or even chest pain. While this may occasionally be a random occurrence, when it becomes frequent and long-lasting, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may be diagnosed.
GERD is a chronic digestive disorder that occurs because the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)—the muscle responsible for keeping stomach contents down—relaxes or functions improperly, allowing acidic contents to enter the esophagus. Over time, this can cause inflammation of the esophageal lining (esophagitis), ulcers, and even increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
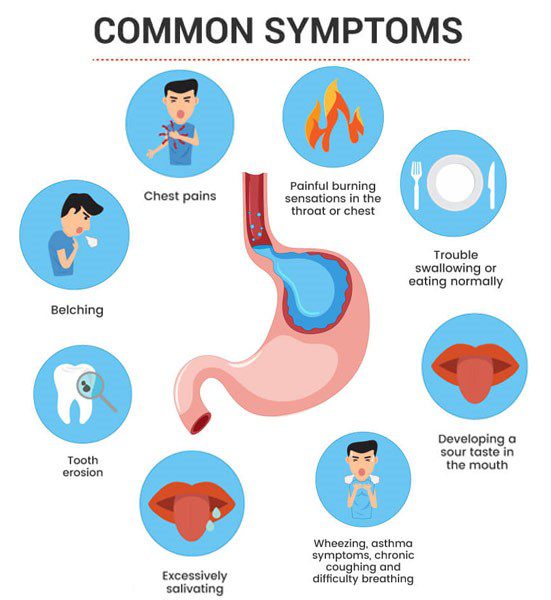
REFLUX SYMPTOMS
Reflux symptoms can vary and may affect people of different ages. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Heartburn – A burning sensation behind the breastbone, often occurring after eating or at night.
- Sour taste in the mouth – This can be due to stomach acid backing up into the mouth.
- Chest pain – Sometimes, reflux can cause pain that may be mistaken for heart problems.
- Difficulty swallowing – This may occur due to inflammation of the esophagus or the formation of scars after prolonged exposure to acid.
- Dry throat or cough – A chronic cough, often occurring at night, can also be related to reflux.
- Bad breath – This can be associated with stomach contents backing up into the esophagus and mouth.
These symptoms may be temporary, but when they become persistent or long-lasting, it is important to seek medical attention.
CAUSES OF REFLUX
The primary cause of reflux is a malfunctioning lower esophageal sphincter. This sphincter typically relaxes only when food or liquid needs to pass from the esophagus into the stomach. However, if it relaxes too often or for too long, stomach acid can return to the esophagus, causing inflammation and other unpleasant symptoms.
Risk factors for reflux include:
- Obesity – Excess weight increases pressure on the stomach, making it easier for acid to rise into the esophagus.
- Pregnancy – The growing fetus can press on internal organs, including the stomach.
- Smoking – Smoking reduces the tone of the LES, allowing stomach contents to more easily enter the esophagus.
- Certain medications – Some medications, such as calcium channel blockers, muscle relaxants, and asthma medications, can influence reflux.
- Poor diet – Eating large quantities of food or consuming certain acidic foods (citrus fruits, tomatoes, alcohol, chocolate) can worsen reflux symptoms.
REFLUX COMPLICATIONS
Although reflux is generally uncomfortable rather than dangerous, long-term and uncontrolled reflux can lead to serious health problems. Some potential complications include:
- Esophagitis – Inflammation of the esophagus due to constant acid exposure. This can cause pain and swallowing difficulties.
- Esophageal ulcers – Prolonged reflux can lead to ulcers in the esophagus.
- Barrett's esophagus – This is a condition where the cells of the esophageal lining change, increasing the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Esophageal strictures – Scarring caused by constant inflammation can narrow the esophagus, making swallowing difficult.
REFLUX DIAGNOSIS
Reflux can be diagnosed in several ways. The first step typically involves a thorough evaluation of the patient's symptoms and a physical exam. The doctor may recommend certain tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the condition of the esophagus:
- Endoscopy – During this test, the doctor uses a flexible tube with a camera to examine the esophagus, stomach, and the initial part of the small intestine.
- pH Test – This test measures the acidity in the esophagus and can help determine how frequently acid returns to the esophagus.
- Barium X-ray – The patient drinks a barium solution, which helps detect abnormalities in the digestive tract during an X-ray examination.
REFLUX TREATMENT METHODS
Reflux treatment can vary depending on the severity of the symptoms. The most commonly used methods include:
Lifestyle changes
- Diet – Reduce the intake of fats, caffeine, chocolate, alcohol, and acidic foods.
- Eating habits – Eat smaller portions, avoid late dinners, and prevent the stomach from becoming overly full.
- Weight loss – Even a small reduction in weight can help alleviate reflux symptoms.
- Sleeping position – Sleeping with the head elevated can reduce acid reflux at night.
Medications
- Antacids – These medications neutralize stomach acid and quickly relieve symptoms, but they only provide short-term relief.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) – These medications reduce the production of stomach acid and are one of the most effective forms of treatment.
- H2 receptor blockers – These also reduce stomach acid production but have a shorter effect than PPIs.
Surgical treatment
If medications and lifestyle changes do not provide the desired relief, surgery may be considered. One of the most commonly performed surgical methods is fundoplication, where the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to strengthen the LES.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/heartburn-treatments-1742754-v1-5c77264646e0fb0001edc787.png)
HOW TO PREVENT REFLUX?
Reflux can be managed and often prevented by following certain preventive measures. Here are some ways to reduce the risk of reflux:
- Balanced diet – Avoid foods that may increase acidity, such as fats, acidic fruits, spicy foods, chocolate, and caffeine.
- Proper meal timing – Avoid eating large meals before bedtime. Try to eat at least 2–3 hours before going to sleep.
- Weight control – Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, so losing weight can help prevent reflux.
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol – These substances weaken the LES and increase the risk of reflux.
- Regulating physical activity – Avoid overly intense physical activity immediately after meals, as this can cause acid to move upward.
Reflux is a common digestive disorder, but its symptoms can be controlled and even prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper diet. If reflux symptoms become persistent or severe, it is essential to consult a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and select appropriate treatment.
INFORMATION SOURCES
- Fass, R., & Tougas, G. (2002). GERD: Practical Therapeutic Management. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 69(Suppl 5), S35–S43.
- Katz, P. O., Gerson, L. B., & Vela, M. F. (2013). Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 108(3), 308-328.
- Vakil, N., Van Zanten, S. V., Kahrilas, P., Dent, J., & Jones, R. (2006). The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A global evidence-based consensus. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 101(8), 1900-1920.
# refliuksas # skrandis #virškinimas