What to do when reflux interferes with sleep?
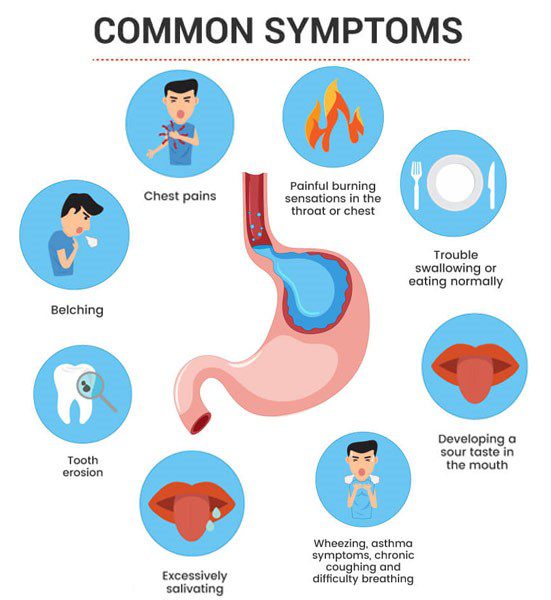
Reflux symptoms
Reflux can present with a variety of symptoms. The most common of them are:
- Heartburn is a burning sensation in the center of the chest that may spread to the throat. Heartburn often occurs after eating and can be particularly severe in the evening.
- Dysphagia - difficulty swallowing. Individuals may feel that food is "stuck" in the throat.
- Regurgitation - sour or bitter taste in the mouth, especially when lying down or bending over.
- Chronic cough is a non-specific symptom that can occur due to acid irritation of the esophagus.
- Changes in the voice - long-term exposure to acid can damage the vocal cords and cause changes in the timbre of the voice.
- Heaviness or pain in the chest - can sometimes be mistaken for a heart attack.
- Inflammation of the mucosa - long-term acid exposure can cause inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, called esophagitis.
In addition to the above symptoms, reflux can also cause other problems such as weakening of the tooth enamel, sore throat and laryngitis. It is important to remember that these symptoms can be individual and not everyone has the same symptoms.
In some cases, reflux can be less obvious, with unusual symptoms such as severe chest pain, asthma symptoms, or even trouble sleeping due to nighttime heartburn. In such cases, the diagnosis can be more complicated and requires a careful examination by the doctor and specialized diagnostic methods, such as endoscopy, pH measurements or esophageal manometry.
What causes reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or simply reflux, is a complex condition involving many different factors. The main cause is failure of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular structure that regulates the flow of food from the esophagus to the stomach and prevents stomach contents from backing up into the esophagus. This sphincter can malfunction for various reasons:
- High stomach acidity – High levels of stomach acidity can promote relaxation of the sphincter.
- Hormonal changes - LES tone can change during pregnancy or due to certain hormonal disorders.
- Muscle weakness – Age-related muscle weakness can weaken the LES.
- Excess fat around the abdominal area - Being overweight and obese increases pressure in the abdominal cavity, which can force stomach contents back up into the esophagus.
- The use of certain medications, such as anticholinergics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and others, can relax the LES.
- Dietary habits - fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol and smoking can also contribute to LES relaxation.
- Genetic predisposition - families with more members with GERD are more likely to have the problem in the next generation as well.
The most vulnerable groups of persons are:
- Obese persons - higher body weight especially increases intra-abdominal pressure, which can directly provoke reflux.
- Pregnant women - hormonal changes and the increasing size of the fetus during pregnancy can put pressure on the abdominal organs, which increases the pressure in the stomach.
- Older people - Age-related changes in the body, such as decreasing muscle tone and weakening of the LES, can increase the risk of reflux.
- Smokers - Tobacco smoke can weaken the LES and promote acid reflux.
- Individuals taking certain medications—medications that relax the LES or increase stomach acid—can cause or worsen reflux symptoms.
- Individuals with a hiatal hernia, a condition in which part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. A hiatal hernia can interfere with the normal functioning of the LES and make it easier for stomach contents to back up into the esophagus, making it one of the most common anatomical causes of reflux.
- Occupational risk groups - people whose work nature requires frequent bending or prolonged sitting may experience increased abdominal pressure, which may also contribute to reflux symptoms.
It has also been found that genetic predisposition, chronic stressful conditions and certain eating habits, such as late dinners or large meals before bed, can also contribute to reflux symptoms. From eating habits to lifestyle choices, every aspect can affect the functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the risk of reflux.
These factors can not only cause reflux, but also strengthen its symptoms if the disease has already developed. Therefore, it is important to recognize that reflux may require a complex approach to treatment, including lifestyle changes, dietary regulation and, if necessary, drug therapy.
Dietary tips that can help control reflux symptoms
Diet is an important factor in controlling reflux symptoms. Avoiding certain foods and making dietary adjustments can significantly reduce or control the occurrence of reflux. Here are some nutritional tips that can help control reflux symptoms:
- Limiting fatty foods - Fatty foods slow gastric emptying, which promotes acid production and can cause reflux symptoms. It is recommended to avoid high-fat meat, full-fat dairy products, fried potatoes, cakes and other high-fat dishes.
- Avoiding spicy, sour and fermented foods - Spicy spices, citrus fruits and juices, tomatoes and tomato-based products can irritate the esophagus and promote heartburn symptoms. Vinegar and fermented foods should also be avoided, which can also cause heartburn.
- Smaller and more frequent meals - Instead of three large meals a day, it is recommended to eat smaller portions five or six times a day. This helps reduce the burden on the stomach and reduces the likelihood of food and acid refluxing back into the esophagus.
- Avoid dinner before bed - Eating at least three hours before bed can significantly reduce reflux symptoms at night, as the stomach has enough time to empty before going to bed.
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption - Alcohol and caffeine relax the lower esophageal sphincter, making it easier for stomach contents to back up into the esophagus. Reflux symptoms can be reduced by avoiding these stimulants.
- Water drinking regime - Drinking enough water during the day promotes dilution of stomach contents and easier passage of food. However, it is important to avoid drinking large amounts of liquid during meals, as this can increase stomach contents and pressure.
- Eating a high-fiber diet - Fiber helps regulate the digestive system and can help prevent reflux. Include more fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes in your diet.
- Correcting your position after eating - Sitting up straight or walking after a meal can help the food settle properly in the stomach, preventing it from backing up into the esophagus. Avoid bending over or lying down for at least three hours after eating.
- Weight control - Overweight and obesity are known to be one of the main risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Being overweight increases the pressure in the abdominal cavity, which promotes the return of stomach contents into the esophagus. Effective weight loss can significantly improve or even eliminate reflux symptoms.
- Avoid smoking - Nicotine in cigarette smoke weakens the lower esophageal sphincter, thus promoting heartburn. Quitting smoking can be one of the most effective ways to reduce reflux symptoms.
- Diet diary - Keeping track of what foods or drinks trigger or worsen your reflux symptoms can help you customize your diet plan. Write down what you eat and when, as well as the time and intensity of symptoms.
- Lunch as the main meal of the day - In order to reduce the likelihood of reflux, it can be useful to consume a larger portion of food during the day, and dinner should be lighter and no later than a few hours before bedtime.
- Include plant-based foods - Plant-based foods such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, and grains are lower in fat and do not stimulate stomach acid production as much as animal-based foods.
- Consuming natural antioxidants and anti-inflammatories - Products that contain natural antioxidants, such as green tea, fish oil and olive oil, can help reduce inflammation in the esophagus.
These dietary tips are general and can help many people with reflux symptoms, but each person's response to food may be different. Therefore, it is important to consult with a gastroenterologist or nutritionist who can provide personalized advice based on your specific health conditions and needs. In controlling reflux, not only dietary changes are important, but also a comprehensive approach to lifestyle changes.
What to do when reflux interferes with sleep?
Reflux can be especially frustrating when it interferes with a night's rest. Symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus are often worse when lying down, due to the decrease in gravity and the horizontal position of the body, which allows stomach acids to enter the esophagus more easily. To reduce the nocturnal effects of reflux and improve sleep quality, it is important to implement several lifestyle and dietary adjustments:
Elevate the position of the head and upper body while sleeping
Sleeping with the head and upper body elevated makes it harder for stomach contents to back up into the esophagus. This can be achieved by using special pillows or by raising the legs of the head of the bed about 15-20 centimeters high so that the entire bed is slightly tilted.
Avoid eating before bed
Eating should be avoided for at least 3-4 hours before bedtime. It is important that the stomach is as empty as possible before trying to sleep, as food in the stomach stimulates acid production and can cause reflux symptoms.
Adjust the diet
Dinner should be light and not late. It is recommended to avoid fatty, spicy foods and products that can cause heartburn, such as chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes and alcohol. Caffeine consumption late in the day should also be avoided.
Maintain a healthy body weight
Being overweight, especially in the abdominal area, can increase pressure in the stomach and encourage acid production. Losing weight can help reduce reflux symptoms.
Avoid smoking
Nicotine weakens the function of the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acidic stomach contents to enter the esophagus more easily, especially when lying down.
Drink enough water
Water helps reduce stomach acid and promotes digestion. However, it is important to avoid drinking large amounts of fluids directly before bed, as this can increase the volume and pressure of stomach contents.
Maintain a regular sleep schedule
Going to bed and getting up at the same time every day helps regulate the body's internal clock and improve sleep quality.
Relaxation techniques
Stress can make reflux symptoms worse, so it's helpful to practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation or deep breathing before going to bed.

Following these recommendations can significantly reduce the impact of reflux symptoms at night and improve sleep quality. Additionally, these tips may help:
- Use probiotics and stomach acid neutralizers. It is sometimes helpful to take probiotics, which can improve gut microflora and help regulate digestive processes, or antacids, which neutralize stomach acids and can provide short-term relief from heartburn, especially before bed.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing. Tight clothing, especially around the abdomen, can increase pressure in the stomach and encourage acid to back up into the esophagus.
- Consultation with a specialist regarding medical treatment. If lifestyle changes and dietary corrections do not help, you can consult with your doctor about prescribing medications that reduce stomach acidity or strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter.
- Optimizing the sleeping environment. Make sure the bedroom is quiet, dark and cool. Use a comfortable and high-quality pillow and mattress that supports the correct body position and helps prevent the head and upper body from dropping, which can promote heartburn.
- Monitor and regulate life habits. Keep track of what factors caused or worsened your reflux symptoms. This may include keeping a food diary, tracking your sleep position or trying different relaxation techniques.
Although reflux can be frustrating, using these techniques properly can significantly reduce its effects during the night and improve your overall quality of life. It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personal recommendations and to ensure that the treatment method you choose is appropriate and safe.
Information sources
- "Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)"
- "The Esophageal and Swallowing Disorders, GERD"
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- "Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Comprehensive Overview"
- "GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease"
# refliuksas