How does dementia affect family life?
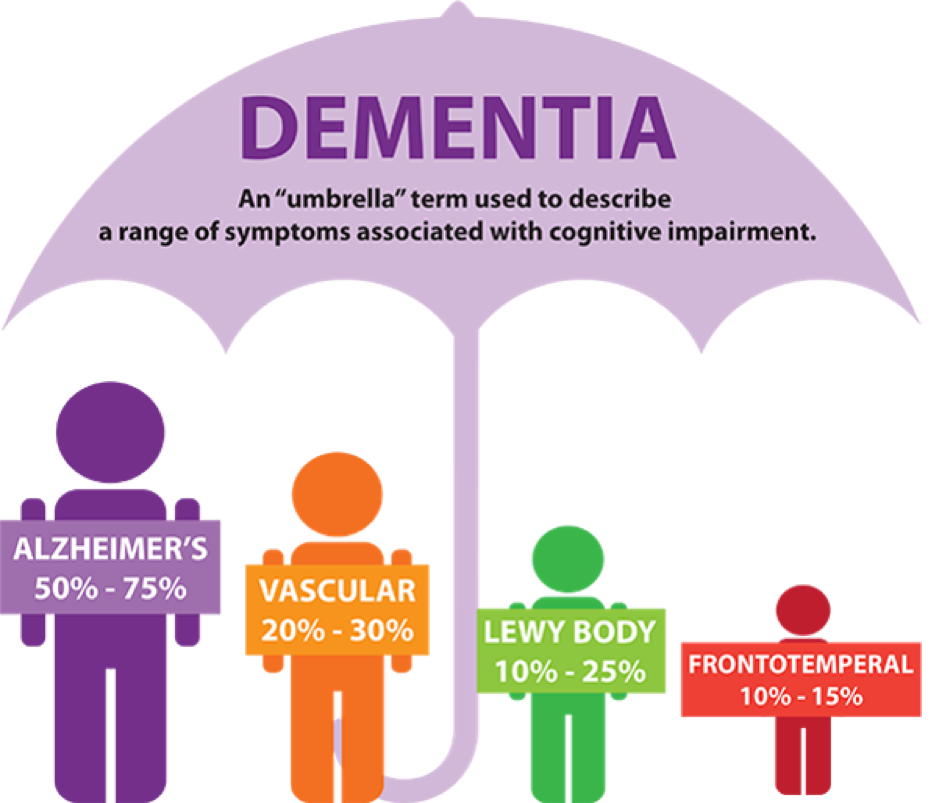
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of all cases. It is characterized by a gradual decline in cognitive functions such as memory, thinking and speech, as well as personality changes. Symptoms may be mild at first, such as mild memory loss, but over time they become more intense and interfere with daily activities.
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia and is caused by problems with blood flow to the brain, such as after a stroke. Symptoms of this form depend on the area of the brain affected and may include problems with planning, decision-making, and speech disorders.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is characterized not only by memory and thinking problems, but also by physical symptoms such as tremors, movement disorders similar to Parkinson's disease, and visual hallucinations.
Frontotemporal dementia tends to affect younger people than other types of dementia and is characterized by changes in personality, behavior and language due to damage to the frontal and/or temporal lobes of the brain.
The progression of dementia is individual and depends on the type of disease, the patient's health and treatment. Dementia usually starts with mild symptoms that become more severe over time. The early stages usually include memory loss, difficulty performing daily activities, and changes in mood and behavior. In the middle stage, symptoms become more prominent, including greater memory deficits, confusion between day and night, and problems with language and comprehension. In the late stage, patients usually become completely dependent on the help of others, with significant difficulties in speaking, walking and performing daily tasks.
Although dementia is a progressive and incurable condition, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life. It is also important to maintain the patient's physical activity, social inclusion and psychological support to reduce the impact of symptoms and improve general well-being.
The impact of dementia on the individual and their family
The impact of dementia on an individual and their family can be complex and multifaceted, including psychological, social and economic aspects.
- One of the main effects of dementia on a person is a gradual decrease in independence. In the initial stages, this may manifest as difficulty remembering recent events, problems planning or organizing tasks. Over time, you may need help with daily activities such as personal hygiene, shopping or housework. This creates great emotional pressure on both the sufferer and their loved ones, as they see their loved one's ability to function independently diminish.
- The psychological impact is also significant. People with dementia may experience depression, anxiety, mood swings or even aggression, which further complicates their daily lives and relationships with family members. Such changes in behavior can cause stress and tension in the family, sometimes even rejection or misunderstanding from relatives.
- From an economic perspective, dementia care is also a major challenge. Long-term care, medical assistance, day care centers, or personal assistance devices can be a financial burden for a family. In addition to the direct medical costs, family members are often faced with the need to reduce work hours or even quit their jobs to care for a sick loved one, adding to the financial pressure.
- Social impact is also important. The sufferer and their family may experience social isolation as dementia can make social interaction and communication difficult. Family members may feel isolated from others because of the need for constant care or because of the fear that others will not understand the difficulties they are experiencing.
Given these challenges, support for people with dementia and their families becomes crucial. This includes both providing information and education about the condition, as well as emotional and practical support. Educating the public about dementia and its effects can help reduce stigma and promote greater understanding and support for sufferers and their families.
Interventions and support strategies are available for both patients and their families
Intervention and support strategies for dementia patients and their family members are a complex and multi-layered process that includes medical, social, psychological and environmental aspects. These strategies aim to improve quality of life, reduce symptoms, help cope with the challenges of daily life, and provide emotional and practical support for both sufferers and their families.
Medical interventions
- Drug therapy: Although there is no cure for dementia, certain drugs can slow the progression of the disease and reduce some symptoms, such as memory problems, speech problems, disorientation, or behavioral changes. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists are often prescribed in the early to moderate stages.
- Symptomatic therapy: Medications and therapies for specific symptoms, such as antidepressants for depression, antipsychotics for behavioral and mood disorders, and treatments for sleep disorders.
Social and psychological interventions
- Memory therapy: Memory therapy and other cognitive tasks can help maintain brain function and reduce the progression of symptoms. These include creating memory books, music therapy, and participating in activities that promote cognitive stimulation.
- Behavioral strategies: Teaching family members and caregivers how to manage problem behaviors (eg, aggression) using non-pharmacological strategies, such as environmental modification, activity planning, and appropriate communication.
- Psychosocial support: Group or individual psychotherapy sessions for both patients and family members to provide emotional support, stress management training, and strategies for coping with the challenges of the illness.
Environmental adaptation
- Creating a safe environment: Modifications to the home to reduce the risk of injury, such as removing carpets that can cause slips, installing adequate lighting, and safety handles in baths and toilets.
- Technological tools: Wearable or in-home technological solutions, such as GPS tracking devices that help track a person's location or automatic medication reminders.
Support from family and caregivers
- Education for family members: Education about dementia, its course, care strategies and behavior management so that family members can effectively care for their loved ones.
- Support groups: Support groups can provide valuable emotional resilience, understanding and a sense of community for both individuals with dementia and their families.
- Professional support and care: After a diagnosis of dementia, it is important to contact social care and health care professionals as early as possible, who can help plan and provide the support you need. This may include home care services, day care centers or long-term care facilities.
An integrative approach to dementia care and support that includes these interventions can help maximize the patient's quality of life and provide needed support to family members. It is important to individualize interventions based on patient needs, disease stage, and family capabilities.

Information sources
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Alzheimer's Association
- National Institute on Aging (NIA)
- The Lancet Neurology
- Journal of Alzheimer's Disease
# demencija