Rheumatoid arthritis and its key risk factors
Rheumatoid arthritis usually manifests symmetrically, affecting both the right and left sides of the body's joints. In its initial stages, rheumatoid arthritis typically affects small joints, such as those in the fingers and wrists, but can progress to larger joints, including the knees, shoulders, and hips.
What are the risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease, and the exact risk factors are still not completely clear, but it is believed to arise from a complex interaction of various genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
- Genetic factors: Genetics play a significant role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Studies indicate that certain genes, such as HLA-DR4, are associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis. While these genes do not directly cause RA, they may increase the propensity for immune system disorders that eventually lead to an autoimmune reaction.
- Immune system disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly recognizes joint tissues as foreign and attacks them. This causes an inflammatory reaction, leading to joint swelling, pain, and eventually damage. Why the immune system begins to function in this way is still not entirely understood.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors may also contribute to the development of RA. For instance, smoking is a known risk factor, especially for individuals with certain genetic traits. Other potential factors include obesity, infections, stress, and certain occupations that require repetitive or heavy joint movements.
- Age and gender: Rheumatoid arthritis can occur at any age, but it most commonly begins between the ages of 40 and 60. Additionally, women are about three times more likely to develop RA than men, indicating a possible influence of hormones on the disease's development.
- Hormonal factors: Rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women than men, suggesting a potential role of hormones, particularly female sex hormones, in the development of the disease. Pregnancy and menopause can also influence the manifestation and course of RA symptoms.
- Infections: Some scientists have speculated that certain bacteria or viruses might initiate an autoimmune reaction in genetically predisposed individuals. While this theory is still under investigation, there is no clear evidence that any specific infection directly causes RA.
- Microbiome: More recent studies suggest that the gut microbiome (the entirety of microorganisms in the gut) may influence the development of rheumatoid arthritis. An imbalance in gut bacteria could affect immune system functioning and promote inflammatory diseases.
- Epigenetic factors: Epigenetic changes, which are changes in gene expression that do not alter the DNA sequence itself, may also influence the risk of RA. These changes can be affected by environmental factors such as diet, stress, and smoking.
Nonetheless, the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis is complex and not fully elucidated. The disease may be caused by a unique combination of various factors in each individual, suggesting that treatment and prevention may require a personalized approach.
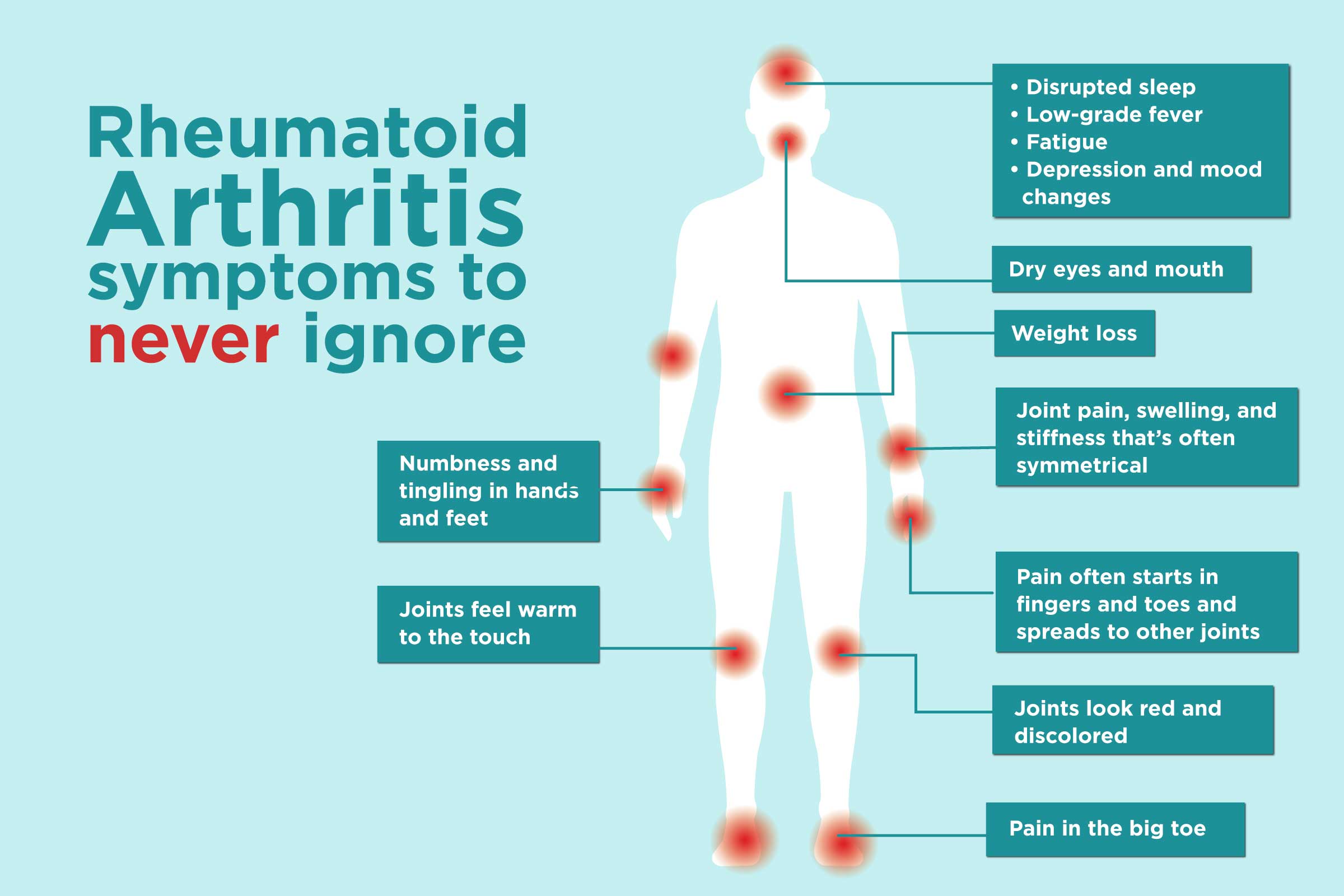
Rheumatoid arthritis and its symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by a multitude of symptoms that can vary from mild to very severe and affect not only the joints but also other parts of the body. These symptoms include:
- Joint inflammation and pain: The primary symptom of RA is joint inflammation, causing pain, swelling, and redness. The pain is usually most intense in the mornings or after a period of inactivity and can worsen with joint activity.
- Joint stiffness: Patients often experience joint stiffness, especially in the mornings or after being inactive for a long time. Stiffness can last for several hours and hinder daily activities.
- Symmetrical symptoms: Rheumatoid arthritis often affects symmetrically, meaning if inflammation occurs in one joint, similar symptoms usually appear in the corresponding joint on the other side of the body.
- Fatigue and general malaise: Rheumatoid arthritis can cause significant fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of malaise, which can interfere with routine activities.
- Joint deformities: As the disease progresses, joint deformities and erosions may occur, causing the joints to lose their original shape and function.
- Joint swelling and inflammation: Inflamed joints can be swollen and warm to the touch. Sometimes, fever may also occur.
- Rheumatoid nodules: Some patients develop hard nodules under the skin, most commonly on the elbows. These nodules are usually painless.
- Problems with other organs: Rheumatoid arthritis can affect not only the joints but also other organs, including the eyes, lungs, and heart. This can cause various symptoms, such as a feeling of dry eyes, chest pain, or breathing difficulties.
- Psychological consequences: Due to chronic pain and reduced mobility, rheumatoid arthritis can also affect mental health, causing depression or anxiety.
RA symptoms can be variable; they can worsen (so-called flare-ups) and then improve. Flare-ups can last several days or weeks and can be difficult to predict. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are very important for managing symptoms and preventing or slowing the progression of the disease.
Lifestyle changes for living with rheumatoid arthritis
Lifestyle changes made when living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are crucial for managing symptoms, maintaining good quality of life, and reducing the impact of the disease. These changes encompass several areas, including diet, physical activity, stress management, and adaptation of daily activities. Here are some key aspects:
Balanced diet
While there is no specific diet to cure RA, a healthy and balanced diet can help manage inflammation and maintain proper weight. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and nuts can help reduce joint inflammation. Vegetables, fruits, and whole grain products should form the basis of the diet, as they provide antioxidants that can help reduce damage caused by free radicals. It's also recommended to avoid processed food and trans fats, which can promote inflammation.
Physical activity
Regular exercise is important for RA patients, as it strengthens the muscles around the joints and maintains joint flexibility. Aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling and muscle-strengthening exercises are recommended. It is important to find the right balance of exercise intensity and duration to avoid overloading the affected joints.
Stress management
Stress can exacerbate RA symptoms and promote inflammation. Therefore, learning stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, yoga, meditation, or deep breathing, is important. Psychological support or counseling can also be beneficial.
Weight control
Maintaining a healthy weight is very important for RA patients, as excess weight can increase pressure on the joints, particularly the knees and hips. A healthy diet combined with regular physical activity can help maintain optimal weight.
Reducing smoking and alcohol consumption
Smoking is a known risk factor for the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, so quitting smoking is very important. Alcohol consumption should be limited, as certain alcoholic beverages can trigger an inflammatory response.
Adapting daily activities
Rheumatoid arthritis can limit the performance of daily tasks. An occupational therapist can help learn new ways to perform daily activities, reducing strain on the joints. This includes using special tools that make tasks easier, such as opening jars or writing.
Adequate rest
Adequate sleep and rest are very important for RA patients. Inflammation and pain can interfere with good sleep, so it's important to create suitable sleeping conditions and practice habits that promote deep relaxation before bedtime.
Proper hydration
Hydration is also important. Adequate water intake helps maintain joint health and can help reduce pain and swelling.
It's important to emphasize that each case of rheumatoid arthritis is individual, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, it is important to collaborate with healthcare professionals to create a personalized plan for lifestyle changes.

Information sources:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR)
# reumatoidinis artritas